Science background gives teachers additional information on the phenomena students explore. Below is an excerpt from this section on cellular respiration.
Cellular Respiration
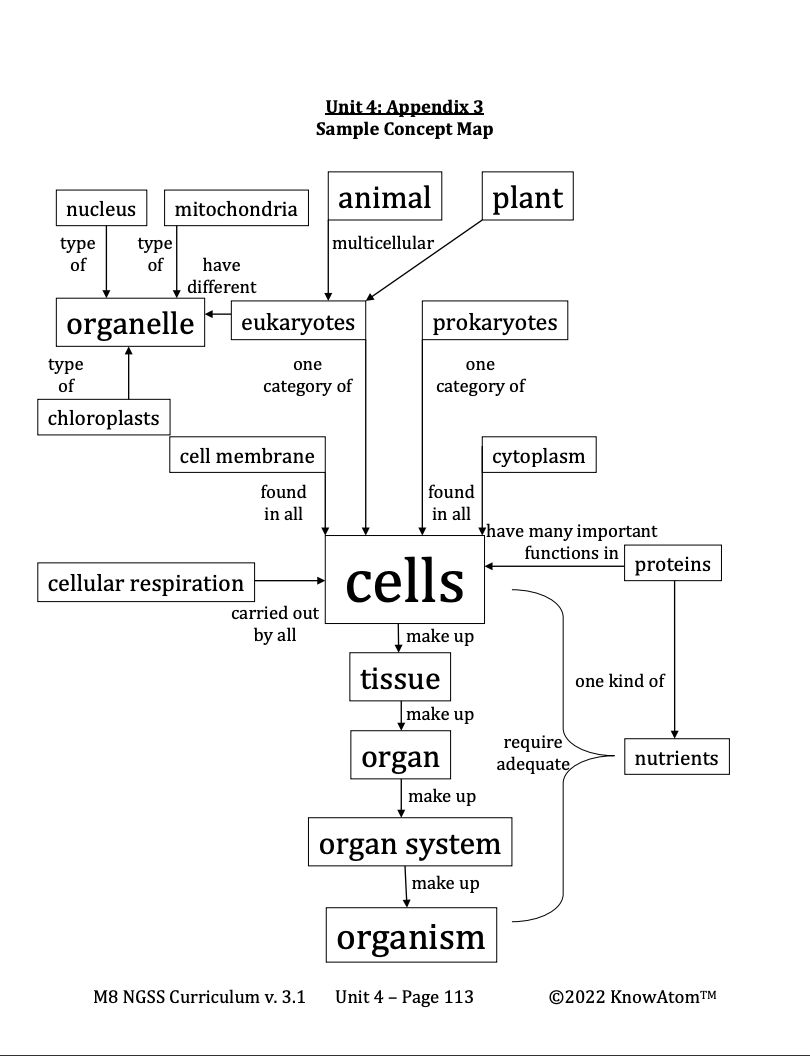
Glucose is an important ingredient in cellular respiration, which is the process in which cells extract energy from food. In cellular respiration within eukaryotic cells, mitochondria use oxygen to convert some of the energy in glucose into energy that is stored in molecules called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. In addition to ATP molecules, carbon dioxide and water are also produced. The carbon dioxide is released as a waste product.
The energy found in glucose cannot be used by cells until it is stored in molecules of ATP. ATP is the molecule that carries energy to where it is needed in the cell. Because of this, cellular respiration is always happening in cells. Without ATP, the cell would not be able to carry out its essential functions, including growing, dividing, and repairing or replacing worn-out organelles.
In humans, cells that need a lot of energy, such as muscle cells, have more mitochondria than cells that don’t need a lot of energy, such as skin cells. Both plant and animal cells store energy they don’t need immediately as fat. Humans generally store several weeks’ worth of energy in their cells.
Cellular respiration that uses oxygen is called aerobic respiration. However, sometimes it can occur when there is no oxygen present. You might have experienced anaerobic respiration when exercising. When there is not enough oxygen present to complete aerobic cellular respiration, muscle cells rely on a process that produces energy without oxygen. A side effect of this process is a burning sensation in your muscles because of a buildup of lactic acid.
Many bacteria, along with some other organisms, can also make ATP without oxygen in a process called fermentation. When yeast and sugar combine in a chemical reaction, ethanol (ethyl alcohol) and carbon dioxide are produced. For example, microscopic yeast cells can grow both with and without oxygen. If there is no oxygen, yeast can chemically break down the simple sugars found in most plants into substances it can use.
During cellular respiration, not all of glucose’s energy is transferred to ATP molecules. About 60 percent is released as heat, which humans and other warm-blooded organisms use to keep our body temperatures steady. While 40 percent might not seem like a lot, many other energy conversion processes are even less efficient. For example, when gasoline is burned, only 25 percent of the energy is used, while 75 percent is released as heat.
Components of Food
Before cellular respiration can happen, however, food molecules are broken down into smaller molecules. Some of those new molecules become part of the organism, helping it to grow and develop. Because of this, food is important because it provides both energy and building materials for organisms.
To understand this, it’s important to first understand that there are three primary components of food: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Carbohydrates are a main source of glucose that your body uses for energy. There are different kinds of carbohydrates. Sugars give your body quick energy. Starches give your body energy that lasts longer. Good sources of carbohydrates include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables. Regardless of the kind of carbohydrate, our bodies turn all of the carbohydrates into glucose that can be turned into energy through cellular respiration.