In this brief lesson, students observe how germinating bean seeds change as they begin to grow. Students will act as scientists as they observe, document, and analyze each step of the germinating process.
In this Life Science unit, Kindergartners explore plants and what they need to live and grow.
This page is a high-level extract of lesson four in which students make models of adult sunflower plants to explore how plants have different parts that help them get what they need to grow. .
This teacher background gives teachers an in-depth explanation of the scientific phenomenon students will learn about in the unit. It seeks to answer the deeper questions that teachers may wish to understand about the concepts being investigated. In this lesson, students explore how a seed grows into a plant.
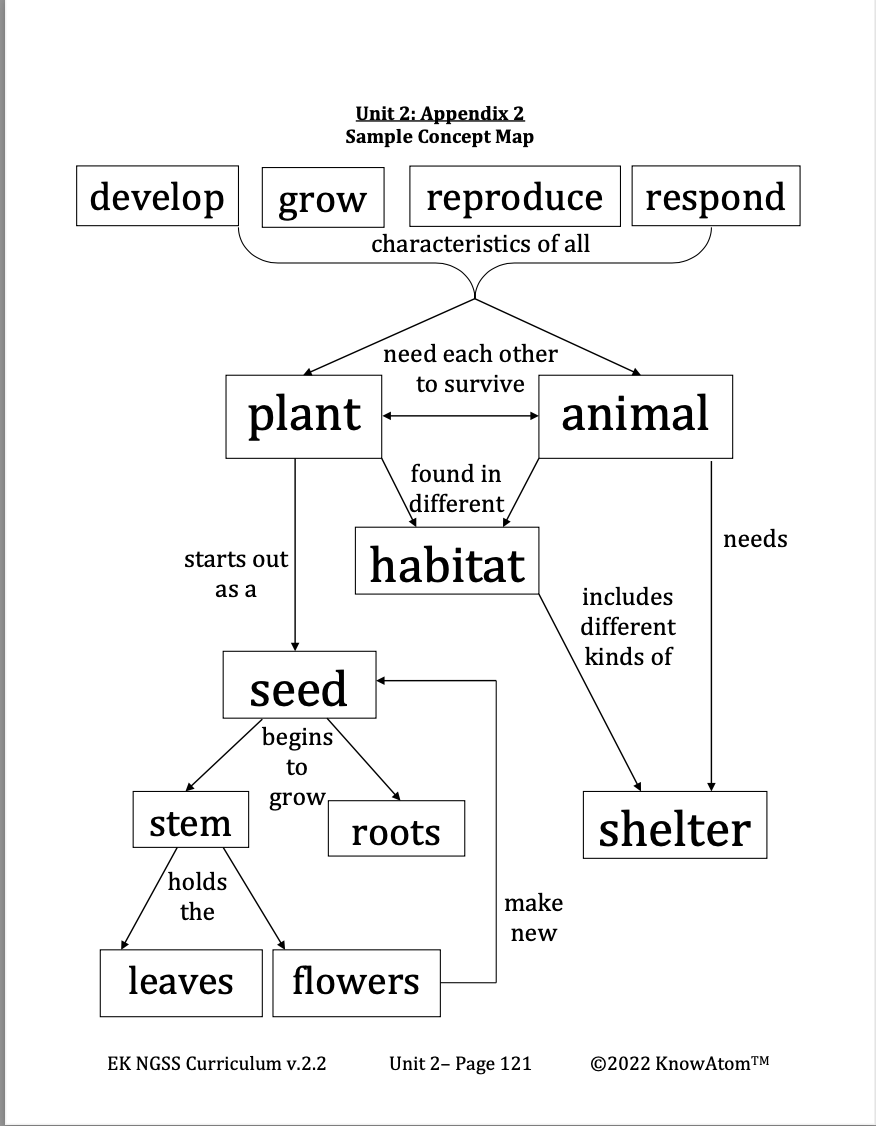
When plants get enough sunlight, air, and water, they will grow and reproduce. There are different ways that plants reproduce. Some plants, such as ferns and mosses, grow from spores, while a few reproduce asexually. Many plants reproduce by producing seeds. Many flowering plants depend on pollinating animals such as bats and many kinds of insects because they cannot make new seeds without pollination. Seeds are young plants inside a protective coat. Seeds have three parts: an outer coat to protect it, one or two cotyledons that store food, and the embryo, which will grow into the new plant.
With enough air and water, a seed will grow into the same kind of plant that it came from. For example, the seeds from carrot plants will grow into carrot plants, while the seeds from apple trees will grow into apple trees. As the seed grows, the plant breaks out of its seed coat and begins to sprout, a process called germination. Plants first grow roots and a stem, and then leaves.
In this brief lesson, students observe how germinating bean seeds change as they begin to grow. Students will act as scientists as they observe, document, and analyze each step of the germinating process.

Prepared hands-on materials, full year grade-specific curriculum, and personalized live professional development designed to support mastery of current state science standards.
Misconception: Plants are not alive because we cannot see them move.
Fact: Plants are alive because they meet all of the requirements for life. For example, there is movement within plants; we just cannot see it.
Flowers : the parts of a plant that make seeds
Leaves : the parts of a plant that collect sunlight and make food
Plant : a living thing that makes its own food from sunlight
Roots : the parts of the plant that hold it in place and take in nutrients and water from the soil
Seed : a young plant inside a protective coat; needs air and water to grow
Stem : the part of a plant that holds the leaves and flowers in place; water and nutrients travel through the stem to the rest of the plant


In this hands-on mini-lesson, students germinate bean seeds to observe how the seeds change as they begin to grow. They carefully observe and record the process each day over a few weeks to notice how the seed germinates and develops into a young plant. This activity helps strengthen students’ understanding of plant parts and functions as they witness each step of the seed growth process.
KnowAtom incorporates formative and summative assessments designed to make students thinking visible for deeper student-centered learning.
Standards citation: NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For States, By States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. Neither WestEd nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.
