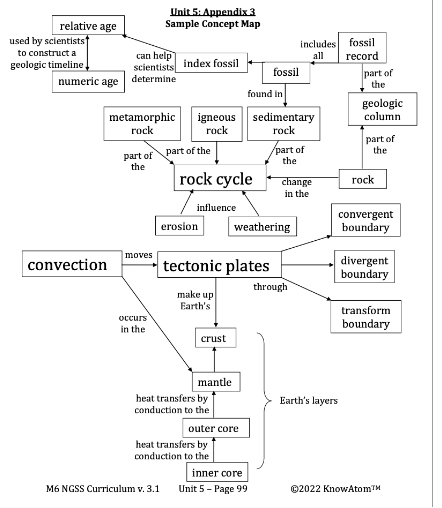
Convection : heat transfer in fluids (liquids and gasses) where warmer, less-dense fluid rises, allowing cooler, denser fluid to take its place; causes a tumbling motion in the fluid
Convergent Boundary : a plate boundary formed when two tectonic plates move toward one another perpendicular to the fault line
Crust : Earth’s outermost layer; the hard rock layer of the planet that makes up the continents and holds the oceans
Divergent Boundary : a plate boundary formed when two tectonic plates move apart from one another perpendicular to the fault line
Igneous Rock : a category of rock formed when hot liquid rock (either magma of lava) cools into solid form
Inner Core : the hottest layer inside Earth; made of a mixture of solid iron and nickel
Mantle : the layer of Earth between the outer core and the crust; mostly molten, semi-solid rock called magma that is so soft it moves in convection currents, like liquid water
Metamorphic Rock : a category of rock formed in chemical reactions where one type of rock is changed by pressure or heat into a new type of rock with different properties
Outer Core : the outer layer of Earth’s core; made of liquid iron and nickel metal
Rock Cycle : the processes that form, break down, and re- form rock from one category to another
Sedimentary Rock : a category of rock formed from layers of sand, soil, clay, gravel, and other sediment that built up in one location over time
Tectonic Plates : drifting slabs of solid rock, called plates, that make up Earth’s surface
Transform Boundary : a plate boundary formed when two tectonic plates slide past each other in parallel, grinding along their sides as they move