Science background gives teachers more in-depth information about the phenomena students explore in this unit. Here is an excerpt of the science background information for this lesson on magnets and motors.
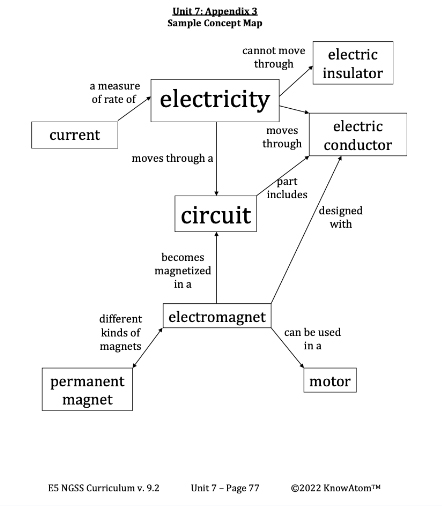
Electric current produces a magnetic field when negatively charged electrons in a conductor move in the same direction. That movement produces a magnetic field around the conductor, which attracts or repels other magnets and objects that contain iron or steel.
All magnets have two magnetic poles—a north pole and a south pole. The rules of magnetism are that opposite poles attract and like poles repel. This means that the north pole of one magnet always attracts the south pole of another, but two north poles always repel each other, as do two south poles.
Magnets are useful in many different applications because they can attract or repel other objects without touching. There are different kinds of magnets. Permanent magnets are objects that stay magnetized without electricity.
Natural magnets are magnetized rocks. Temporary magnets act like a permanent magnet when they are within a strong magnetic field. They lose their magnetism when the magnetic field goes away. Paperclips and iron nails are temporary magnets.
Finally, electromagnets are tightly wound coils of wire that produce a magnetic field when electricity passes through the wire. That electricity is produced in a circuit.
The magnetic field around a straight wire is not very strong. However, if the wire is wrapped in a coil, each turn of the coil produces a magnetic field. The magnetic field of each coil combines to create a strong magnetic field when electricity passes through the coil. Electromagnets are useful because the magnet can be turned off and on by switching the circuit off or on.
Electromagnets are the key to how doorbells work. A simple analog doorbell often includes a battery, wires, an electromagnet connected to a magnetic clapper, and something that makes noise, such as a bell. When you push the doorbell’s button, you close the circuit. This closing of the circuit causes electricity to flow through the doorbell system, which magnetizes the electromagnet and produces a magnetic field around the electromagnet. This magnetic field pulls on the magnetic clapper, causing it to strike the bell. This is what makes the doorbell’s noise. The movement of the clapper striking the bell also opens the circuit. This stops the flow of electricity. As a result, the electromagnet is no longer magnetized.
Magnets are part of many electronic devices because they are used to drive small motors. A motor is a machine that transfers an input of energy into an output of kinetic energy. In an electromagnetic motor, electrical energy is transferred into kinetic energy. A basic electromagnetic motor has two parts: a permanent magnet and an electromagnet. The electromagnet becomes magnetized when it is connected to an electrical current. It then spins rapidly because it is surrounded by the permanent magnet. If a gear is attached to the spinning electromagnet, the gear can be made to do work.