
In this unit, students focus on how sound energy is transferred from one place to another in waves. In this engineering lesson, students apply what they have learned about sound energy to design a sound absorbing wall. This page highlights each component of this lesson.

In this unit, students focus on light energy, investigating the science phenomena of how light moves when it interacts with different kinds of matter. Students use scientific knowledge about light to engineer a device that uses mirrors to redirect light. This page is a high-level extract of this lesson.

In 6th grade, students become scientists and engineers as they investigate the answers to different questions and use their scientific knowledge to solve problems. In this unit, students focus on the relationship between gravity and motion, tracing how gravitational potential energy transforms to kinetic energy in different energy systems. Before exploring these phenomena, students are introduced to the scientific process as they set up their laboratory notebooks. This page provides a snapshot of this lesson.
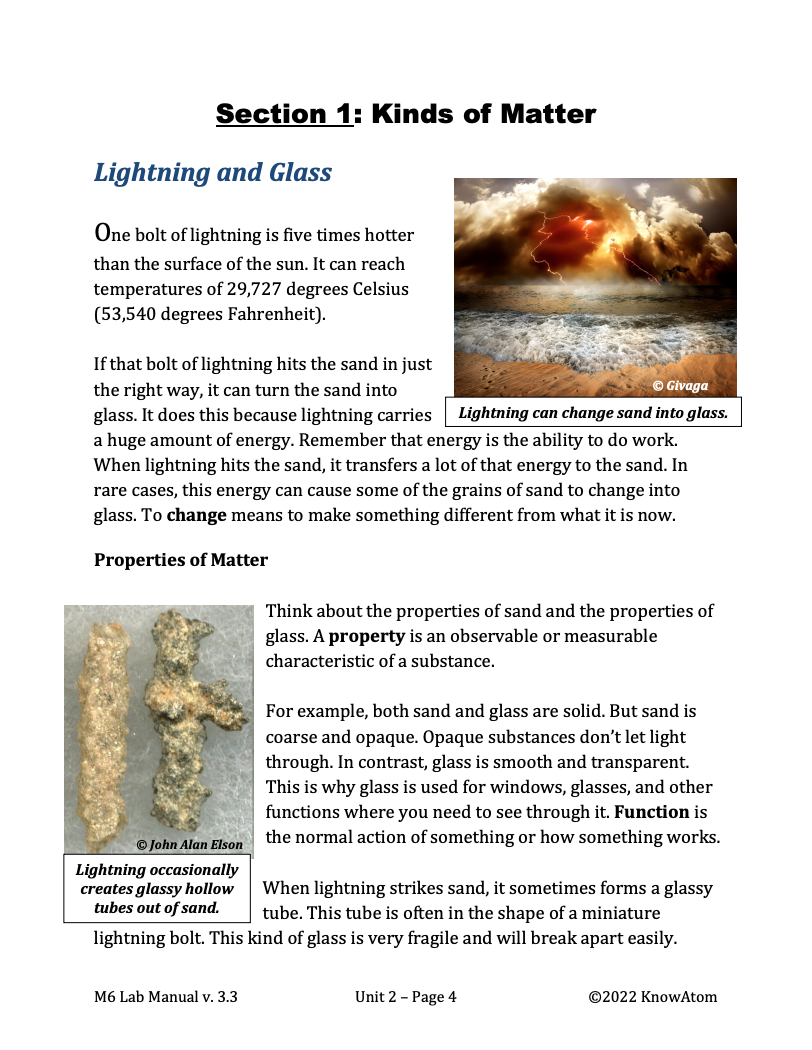
In this unit, students build on their knowledge of energy by exploring the relationship between energy and matter. In this lesson students conduct an investigation into the science phenomenon of how energy is transferred in an endothermic reaction. This page provides an overview of this lesson.

In this unit, students focus on the Earth-Sun-moon system to explore how gravity pulls objects including satellites into orbit. In this lesson, students engineer an insulating solution for a prototype satellite that minimizes the amount of thermal energy transferred into or out of it.

In this unit, students explore the science phenomena of matter, energy, and heat transfer to explore weather and climate. In this lesson they investigate how the sun powers the global water cycle, which in turn has very local impacts that affect regional climates around the world. This page is a high-level extract of this lesson.

In this unit, students investigate the relationship between the water cycle, ocean salinity, weather, and climate. In this lesson, students explore ocean salinity and analyze how ocean density is related to its molecular structure. This page highlights key components of this lesson.
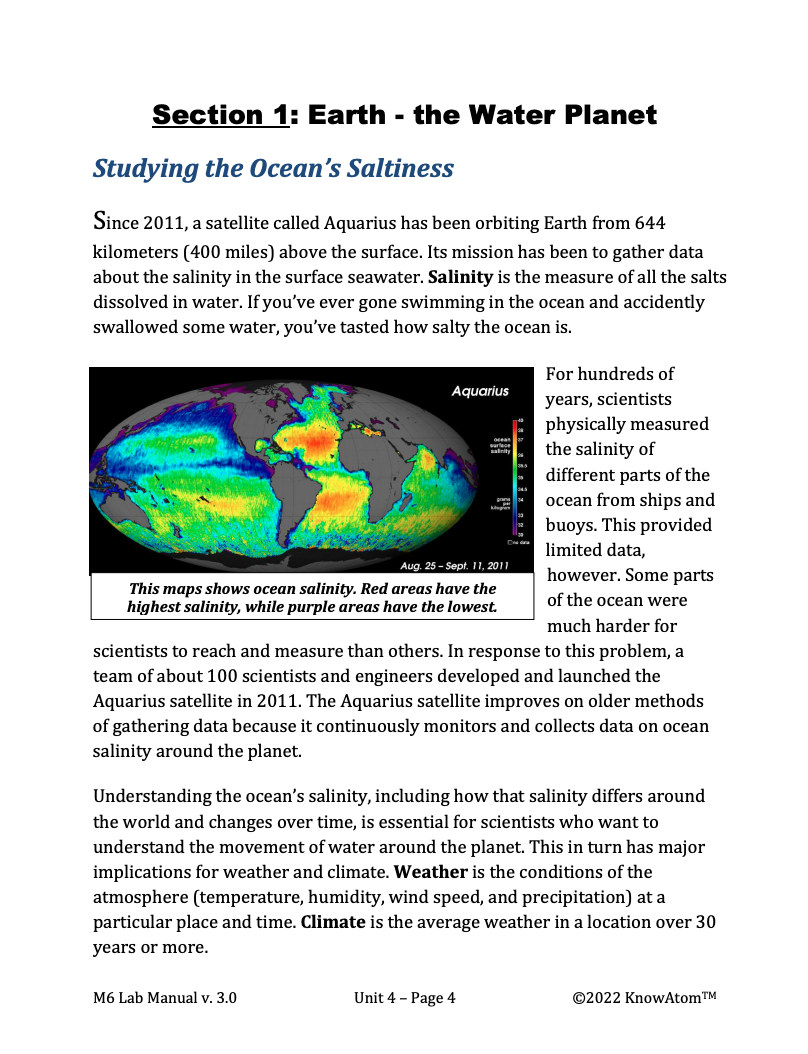
In this unit, students build on their scientific knowledge about matter, energy, and heat transfer to explore science phenomena related to weather and climate. They investigate how the sun powers the global water cycle, which in turn has very local impacts that affect the phenomena of regional climates around the world. This page showcases all the parts of this lesson.

In this unit, students build on their scientific knowledge about matter, energy, and heat transfer to explore the phenomena of weather and climate. They investigate how the sun powers the global water cycle, which in turn has very local impacts that affect the phenomena of regional climates around the world. They then use that knowledge to figure out and design a technology that solves the problem of drought-related water shortages.

In this unit, students focus on the science phenomena of processes that change Earth’s surface over time. This lesson has students modeling how Earth’s landforms can be created and then broken down by weathering and erosion. This page is a high-level extract of this lesson.
In this unit, students focus on the processes that cycle Earth materials, connecting the movement of water in the water cycle and wind with changes to Earth’s surface through weathering and erosion. In this lesson, students explore the science phenomena of how convection in Earth’s mantle causes the tectonic plates to move, creating many of Earth’s landforms. This page showcases key components of this lesson.

In this unit, students explore phenomena that change Earth’s surface over time, analyzing how weathering, erosion, and convection in the mantle are three phenomena that help to cycle Earth materials. In this final lesson of the unit, students use their knowledge to analyze the science phenomena of rock strata, thus reconstructing Earth’s geologic history. This page showcases components of this lesson.

In this unit, students explore the phenomena of diversity of life on Earth and consider how living things pass on traits to their offspring while also adapting to meet the needs of the environment. In this lesson, students figure out how scientists use the fossil record for clues to how life has evolved over time. This page highlights key parts of this lesson.
Standards citation: NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For States, By States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. Neither WestEd nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.
