
In this unit, students explore the science phenomena of animal behaviors of parents and offspring that help the offspring survive. This page is a high-level extract of lesson two in which students mimic the beaver’s behavior of building dams to design their own dams that solve the problem of flooding.

In 2nd grade, students conduct investigations, carry out experiments, and apply their scientific knowledge to engineer prototype solutions. In this unit, students investigate the science phenomenon of properties of different kinds of matter, connecting a material’s properties with the functions for which it is used.

In this unit, students are introduced to scientific exploration as they observe and test the properties of different kinds of matter. For this lesson, students continue their exploration of properties of matter by classifying different kinds of objects according to observable properties.

In the last unit, students explored the properties of different kinds of matter, connecting a material’s properties with the functions for which it is used. In this unit, students focus on Earth materials and the science phenomena of processes that change them (specifically weathering and erosion).
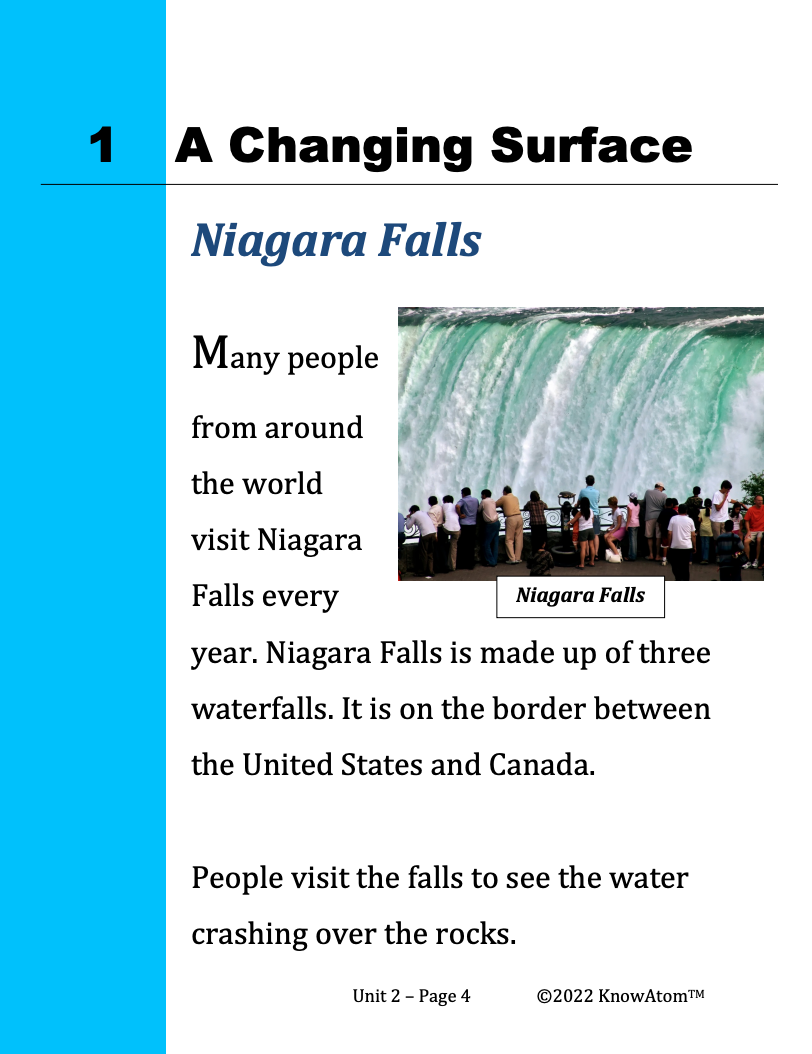
In this unit, students explore the science phenomena of different processes that change Earth’s surface over time. Once students have investigated how wind and water change the shape of the land, they use their scientific knowledge to engineer a solution that prevents rainwater from washing away a sandy hillside. This page showcases key components of this lesson.

In the last unit, students explored how weathering and erosion change Earth materials, and then designed an engineering solution that reduces erosion. In this unit, students are introduced to the science phenomena of landforms on Earth’s surface, exploring how scientists use maps to represent the shapes and kinds of land and water on Earth’s surface.

In this unit, students use the scientific process to analyze Earth’s place in the solar system. They begin by modeling how matter is made up of tiny particles called atoms, and changes state when heat is added or removed. This page provides an overview of lesson 1B in which students explore the science phenomena of how heat affects matter.

In this lesson, students model the solar system and analyze Earth’s place in the system as well as how the force of gravity causes the planets to move around the sun in predictable, regular paths. This page serves to highlight the key components of this lesson.

In this unit, students explore the phenomena of Earth landforms and the water cycle. Once students have modeled landforms and created maps showing the shapes and kinds of land and bodies of water, students analyze how water moves over the land as it flows downhill because of gravity and cycles between solid and liquid depending on the amount of heat present.

In the last unit, students explored patterns in land and water on Earth. They build on that knowledge in this unit with a focus on how living things are found in different habitats around the planet, and how living things depend on both living and nonliving components of their environment for survival.

In the last unit, students explored how living things are found in different habitats around the planet and depend on both living and nonliving parts of their environment for survival. In this unit, students focus on plants. They begin with an experiment that investigates the science phenomena of how light and water help plants grow from a seed into an adult plant, and then focus on the function of flowers, which produce seeds.
Standards citation: NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For States, By States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. Neither WestEd nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.
