.png)
In this unit, students explore the natural processes that cause Earth’s surface to change over time, analyzing how energy causes Earth’s matter to transform and cycle from one form to another. In this lesson, they trace phenomena of how energy is transferred in chemical reactions, which allows scientists to produce ethanol to use as an alternative energy source. This page showcases each component of this lesson.

In this unit, students are introduced to the dynamic nature of ecosystems and how disturbances affect them. In this lesson, students observe the effects of an oil spill on the ability of plants to photosynthesize, which can harm an entire ecosystem. This page is a high-level extract of this lesson.
In this unit, students learn about science phenomena related to ecosystems, studying how all living things interact with and depend on other living things and the environment for survival. In this lesson, students explore how humans can create solutions to protect ecosystems by designing an engineering solution for coastal erosion.This page provides an overview of this lesson.
.png)
In this unit, students focus on the phenomena of rocky shore ecosystems and the science phenomena of how organisms interact. For this lesson, students analyze how adaptations allow for the survival of different organisms, specifically sea star structures. This is a high-level extract of this lesson.
.png)
In this unit, students explore the interconnectedness of the living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem phenomena. In this lesson, they design an experiment to test how heat is transferred in different materials found on the rocky shore. This page provides a brief overview of this lesson.
.png)
In this unit, students focus on interactions between the hydrosphere and the geosphere as they explore the phenomena of groundwater in human development. For this lesson, they engineer a water filtration device to treat samples of simulated polluted stormwater runoff. This page highlights key components of this lesson.
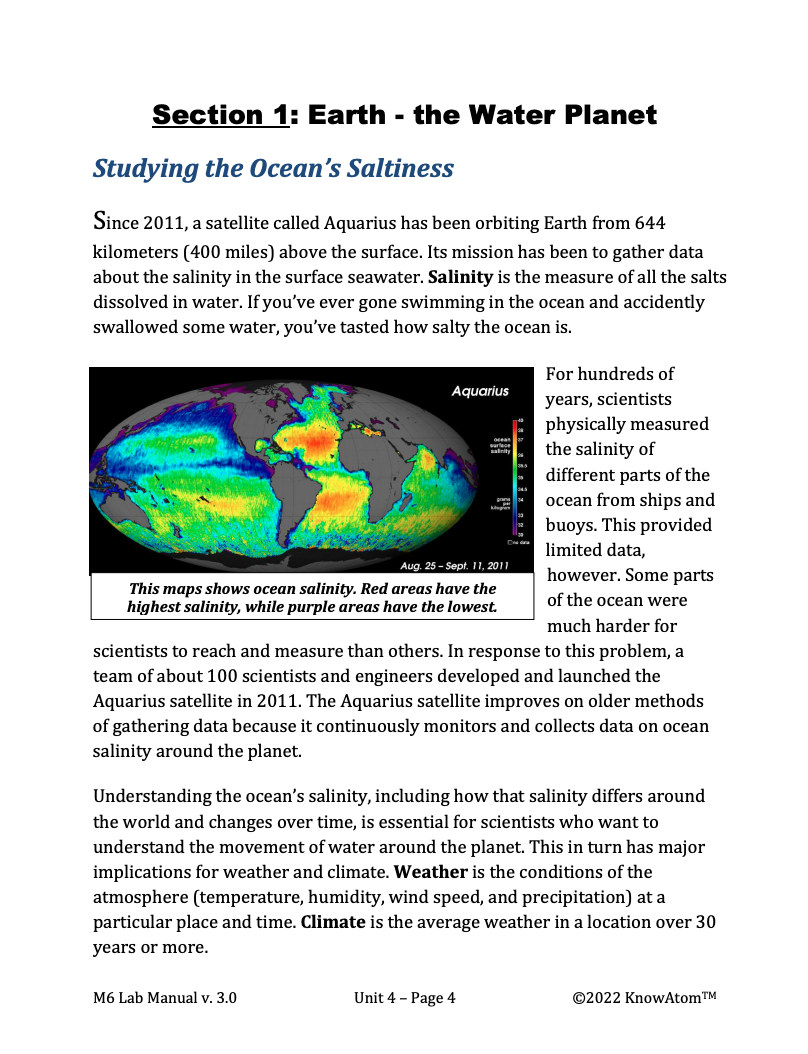
In this unit, students build on their scientific knowledge about matter, energy, and heat transfer to explore science phenomena related to weather and climate. They investigate how the sun powers the global water cycle, which in turn has very local impacts that affect the phenomena of regional climates around the world. This page showcases all the parts of this lesson.

In this unit, students build on their scientific knowledge about matter, energy, and heat transfer to explore the phenomena of weather and climate. They investigate how the sun powers the global water cycle, which in turn has very local impacts that affect the phenomena of regional climates around the world. They then use that knowledge to figure out and design a technology that solves the problem of drought-related water shortages.

In this unit, students explore the phenomena of diversity of life on Earth and consider how living things pass on traits to their offspring while also adapting to meet the needs of the environment. In this lesson, students figure out how scientists use the fossil record for clues to how life has evolved over time. This page highlights key parts of this lesson.
.webp)
In this unit, students use what they know about the relationship between energy and matter to investigate how energy powers the cycling of Earth materials. In this lesson, they analyze the phenomena of processes that form fossil fuels, which determine how these natural resources are distributed around the planet. This page highlights all the parts of this lesson.
Standards citation: NGSS Lead States. 2013. Next Generation Science Standards: For States, By States. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. Neither WestEd nor the lead states and partners that developed the Next Generation Science Standards were involved in the production of this product, and do not endorse it.
